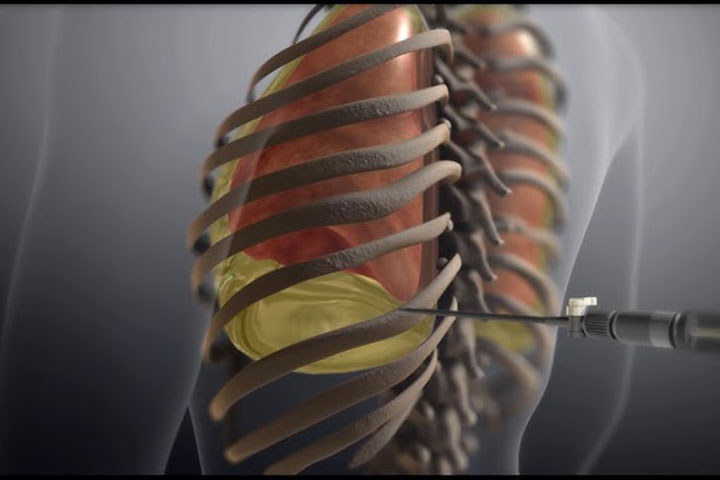
Pleural tapping
Pleural tapping, also known as thoracentesis, is a medical procedure performed to diagnose or treat conditions affecting the pleural space—the thin cavity between the lungs and the chest wall. This space may accumulate excess fluid due to various diseases, leading to symptoms like shortness of breath, chest pain, or coughing.
Book an AppointmentPurpose of Pleural Tapping
Procedure Overview
The patient is positioned either sitting upright or lying on their side to allow safe access to the pleural space.
The area is cleaned, and local anesthesia is administered to minimize pain.
A thin needle or catheter is inserted into the pleural space under ultrasound guidance to withdraw the fluid.
The fluid is sent to the laboratory for tests such as biochemical, microbiological, and cytological analysis.
Common Indications
Risks and Complications
While pleural tapping is generally safe, potential complications include:
Post-Procedure Care
After the procedure, the patient is monitored for any adverse effects, and a chest X-ray may be performed to confirm successful fluid removal and rule out complications.
Pleural tapping is a critical tool in respiratory medicine, providing both relief and essential diagnostic insights, ensuring targeted and effective treatment for underlying conditions.
