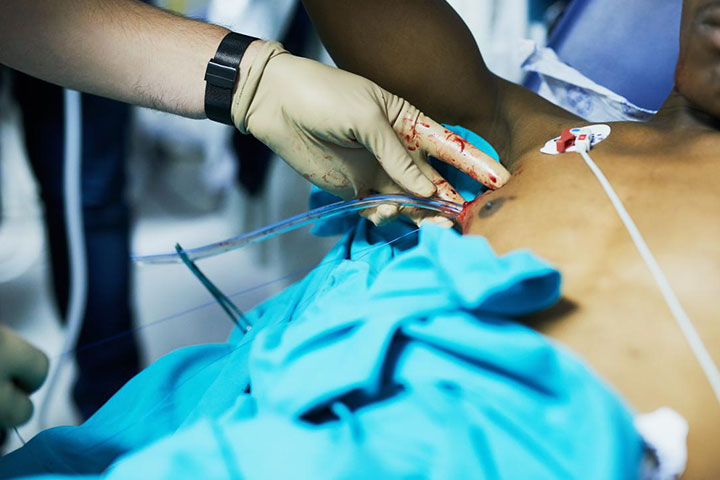
ICD insertion
Intercostal Drainage (ICD) insertion is a medical procedure used to drain fluid, blood, pus, or air accumulated in the pleural cavity (the space between the lungs and the chest wall). It is commonly performed to manage conditions such as pleural effusion, pneumothorax, hemothorax, empyema, or chylothorax.
Book an AppointmentPurpose:
The primary goal of ICD insertion is to restore normal lung function by relieving pressure on the lungs caused by pathological collections in the pleural space. This helps improve breathing, alleviate discomfort, and prevent further complications.
Procedure:
Preparation:
Insertion:
Post-Insertion Care:
Conditions Treated with ICD:
Accumulation of air in the pleural cavity, leading to lung collapse.
Excess fluid in the pleural space due to infection, heart failure, or malignancy.
Collection of blood in the pleural cavity, often due to trauma.
Pus accumulation in the pleural space caused by severe infection.
Leakage of lymphatic fluid into the pleural cavity.
Complications:
While ICD insertion is generally safe, potential complications include infection, bleeding, or injury to nearby structures. These risks are minimized by skilled performance of the procedure and diligent post-procedural care.
